
Concentration of the OreĪccording to the modern concept of atomic structure, electrons in an atom reside in different orbitals. Whereas pera nitrophenol is not water volatile.Ĭompounds that have entermolecular hydrogen bonding are often insoluble in water or have low solubility in water.Įxample: The solubility of aurtho nitrophenol in water is less than that of pera nitrophenol in water. The melting point of aortho nitrophenol is 45☌ while the melting point of pera nitrophenol is 114☌. Similarly, intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs in selycylaldehyde and celycilic acid.Ĭompounds that have intramolecular hydrogen bonding usually have low melting and boiling points and are volatile.Įxample: Intermolecular in aortho nitrophenol and intramolecular hydrogen bonding in per nitrophenol. If the atoms of hydrogen and the negative electronegative element, between which hydrogen bond is formed, are part of a molecule of a compound, then this type of bonding is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding.Įxample: Intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs in ortho nitrophenol. Therefore, these types of compounds are usually soluble in water. Compounds which have intermolecular hydrogen bonding, when water is added to them, the molecules of the compound form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Therefore, the boiling points of HF and H 2O are higher than those of HCl, H 2S and NH 3. N, Cl and S are not so strongly negatively electronegative elements and hydrogen bonding in NH 3, HCl and H 2S is not very or very weak. Therefore, intermolecular hydrogen bonding takes place in HF and H 2O. In HF and H 2O there are hydrogen bonds between atoms of different molecules. The reason for this is that F and O are strongly negatively electronegative elements, so hydrogen bonding is present in HF and H 2O. In other words, the boiling points of HF and H 2O are higher than those of NH 3, HCl and H 2S. Gauss Law or Gauss Theorem : Solid Angle and Electric FluxĮlectrolysis : Definition, Principle and Electrolytic CellĪdsorption : Adsorption rate, Physisorption and ChemisorptionĮlectric Cell : E.M.F., Terminal Potential, Internal Resistance Therefore, the melting and boiling points of such compounds are often high.Įxample: HF and H 2O are liquids at room temperature and NH 3, HCl and H 2S are gases.Įlectric Potential Energy : Electric Dipole, Potential GradientĬoulomb's Law : Electric Field, Potential Difference, Volt Therefore, more energy is required to separate the molecules of these compounds. If the atoms of hydrogen and negative electronegativity between which hydrogen bond is formed are part of different molecules of a compound, then this type of bond is called intermolecular hydrogen bonding.Įxample: Intermolecular hydrogen bonding occurs in HF and H 2O.Ĭompounds which have intermolecular hydrogen bonding, their molecules are attracted to each other due to hydrogen bonding. The following is the sequence of occurrence of negative energies of the major elements.

When the negative power is high, the strength is high. The strength of hydrogen bond depends on the negative electronegativity of the negative electronegativity element.
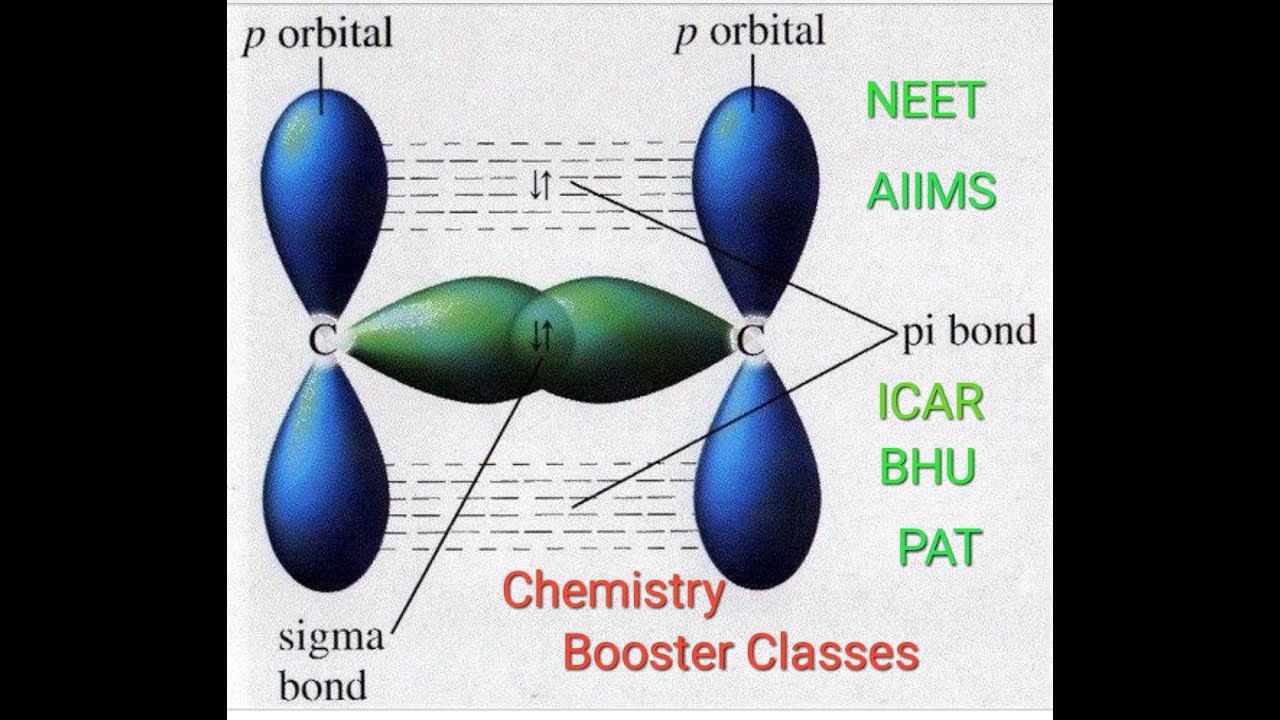
In this case, the atomic negative electronegativity of Hydrogen forms a bridge between the two atoms of the element. This type of bond is called hydrogen bond and it is represented by dotted lines ( – – -). That atom of hydrogen which is connected to an atom of a negative electronegative element by covalent bond, can also be attached to any other atom of that negatively electronegative element by means of a stable electrostatic attraction force. For this reason, there is a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the atom of the negative electronegative element.Įxample: In Hydrogen Fluoride (HF), the bond formed between H and F is a polar covalent bond and due to this there is a partial positive charge on H and a partial negative charge on F.
The bond which is formed between an atom of hydrogen and an atom of a negative electronegative element due to the mutually stable electrostatic attraction force of their partial positive and negative charges, is called hydrogen bond.Ī covalent bond between a hydrogen and an atom of a strongly electronegative element is a polar covalent bond.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
